What Is E-Invoicing and Why It Matters in 2025
The 2025 Budget, due on 26 November 2025, is expected to have far-reaching effects on the UK economy.
Alongside potential tax increases, a major focus will be the continued expansion of HMRC’s digital strategy — particularly through Making Tax Digital and the growing use of e-invoicing.
Across the world, over 80 countries already use the new systems, with the EU introducing a bloc-wide mandate from July 2030.
In the UK, e-invoicing remains mostly voluntary, although certain industries and larger organisations — especially those involved in international trade — have already made the switch.
Transactions involving public entities such as the NHS, government departments, and local councils must already be handled using e-invoicing. HMRC’s long-term plan is to expand and standardise this approach, eventually allowing invoices to be submitted directly to HMRC in real time.
The Practical Benefits of E-Invoicing
E-invoicing allows businesses to process and receive payments faster and with fewer errors.
Under this system, invoices are generated and transmitted electronically, often in PDF, XML, or JSON format.
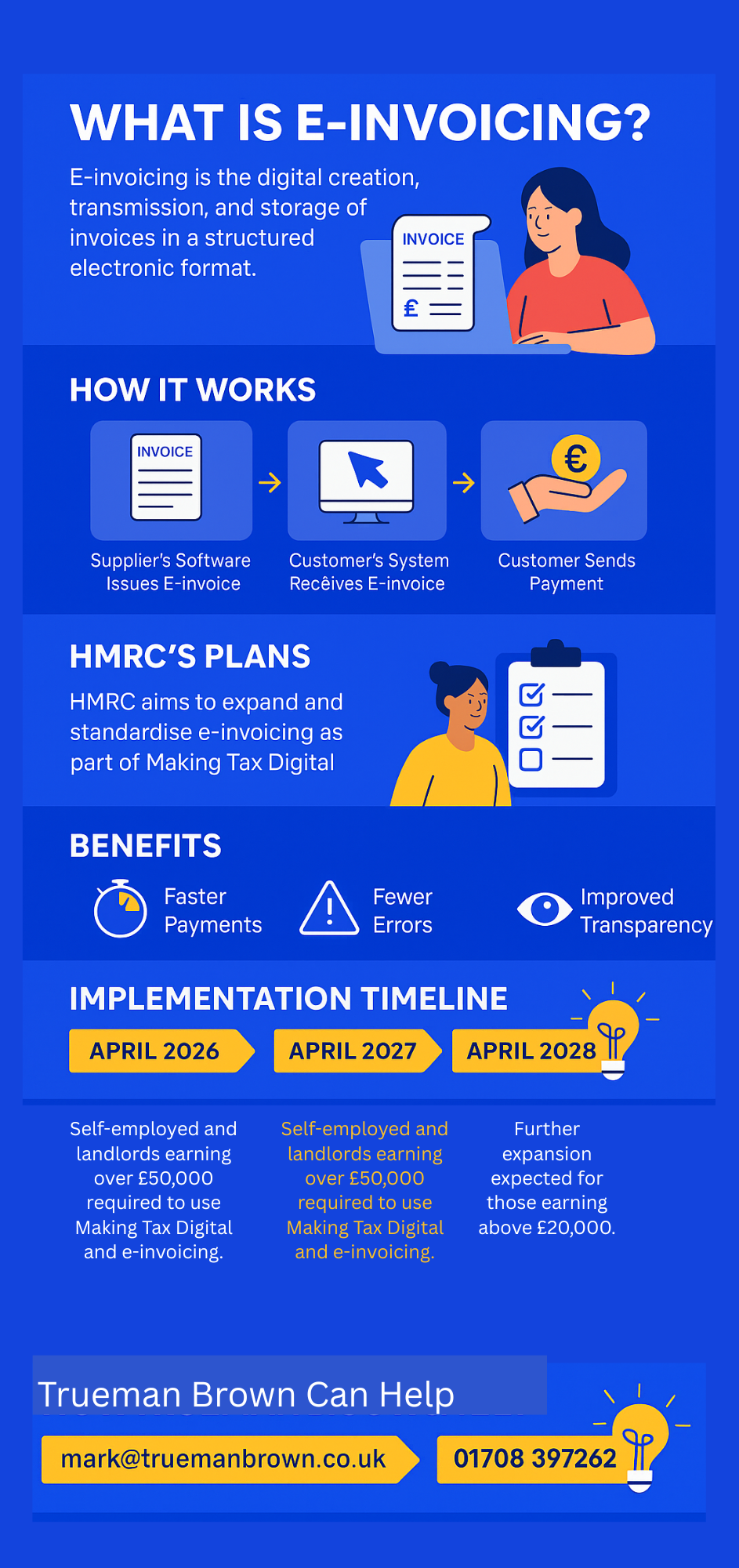
The process is simple: the supplier’s software issues the invoice, the buyer’s system receives and verifies it, and payment follows — often within hours rather than days.
This streamlined digital process eliminates common issues like lost paperwork, delayed payments, and manual input errors.
The overall result is greater efficiency, compliance, and transparency across the invoicing cycle.
HMRC’s Vision
The government has outlined its ambition to make the new system a central part of the UK’s tax system.
In a recent consultation, HMRC cited “improved efficiency, accuracy, and transparency” as key drivers behind the move.
Stakeholders were invited to provide feedback on which invoicing model would best suit the UK, with three main options currently under consideration:
-
Four-corner model: Both supplier and buyer use approved software providers to exchange invoice data securely.
-
Centralised model: Taxpayers send data to certified third parties authorised by HMRC to review and timestamp invoices.
-
Data-sharing model: Businesses transmit e-invoicing data directly to HMRC in real time, with each invoice digitally signed and uniquely stamped before being sent to the customer.
Implementing E-Invoicing in Practice
HMRC views the new system as a natural extension of Making Tax Digital (MTD).
It’s likely that the system will start on a voluntary basis, gradually becoming more widespread as digital infrastructure matures.
Businesses already submitting VAT returns digitally under MTD will experience minimal disruption, while others — especially cash-based traders — will need to adjust.
These businesses will be required to generate digital invoices via apps, record payments, and ensure that every invoice is properly logged and transmitted to HMRC.
The MTD rollout continues:
-
From April 2026, self-employed individuals and landlords earning over £50,000 will be required to comply.
-
From April 2027, the threshold drops to £30,000.
-
By April 2028, it’s expected to extend to those earning more than £20,000.
The Practical Reality: Opportunities and Concerns
HMRC believes that mandating e-invoicing will reduce the UK’s “tax gap” by simplifying tax reporting, cutting down on errors, and supporting compliance.
However, critics argue that new mandates could bring additional administrative pressure, particularly on small businesses with limited digital resources.
The key will be balance — ensuring that businesses reap the benefits of automation and accuracy without being overburdened by complex new requirements.
How Trueman Brown Can Help You with E-Invoicing
Transitioning to e-invoicing can feel daunting, especially with evolving HMRC requirements.
That’s where Trueman Brown can help.
Our experienced tax advisors can:
-
Guide you through the setup and compliance
-
Help you integrate digital invoicing into your existing systems
-
Ensure your processes align with Making Tax Digital requirements
-
Support small businesses and landlords adapting to new digital tax rules
📧 Email: mark@truemanbrown.co.uk
📞 Call: 01708 397262
We’ll help you make a smooth, compliant transition to e-invoicing while keeping your operations efficient and stress-free.
FAQs About E-Invoicing
1. What is e-invoicing?
E-invoicing is the digital creation, transmission, and storage of invoices in structured electronic formats such as XML or JSON. It replaces paper or PDF invoices with automated, real-time processing.
2. Is e-invoicing mandatory in the UK?
Currently, e-invoicing is mandatory only for transactions involving public sector entities, though HMRC plans to expand this requirement across the private sector in the coming years.
3. What are the main benefits of e-invoicing?
Faster payments, fewer errors, improved transparency, and easier tax compliance.
4. How can I prepare for e-invoicing?
Review your current accounting software, ensure it supports digital invoicing, and start digitising your invoicing process early to stay ahead of regulatory changes.
5. Can Trueman Brown assist with implementation?
Yes. Trueman Brown offers tailored advice and support for businesses looking to implement the new system efficiently and compliantly.

Recent Comments